Preventive Measures And Controls For Food Safety
Food Safety is one of the most critical problems for the food industry, and prevention is the key. Unfortunately, there’s no such thing as a 100% fool-proof way to prevent foodborne illnesses. But there are ways to reduce the risk and avoid common mistakes that can lead to food contamination. Food businesses can take several simple steps to help prevent foodborne illnesses. According to WHO’s estimation, there are at least forty-two thousand people who die from foodborne illness in the world every year.
As a food business owner, preventive measures and controls are a better way to reduce the risk and harm to your business. Improving food safety benefits customers and protects anyone downstream of the manufacturing process which handles food. It can also protect people and animals exposed to microbes that may have been inadvertently introduced into the food. Follow these six steps to produce safe foods and help keep your products clean. For an in-depth understanding of Critical Control Points (CCPs), consider reading our comprehensive article: [https://safefood360.com/blog/understanding-the-difference-between-prp-oprp-ccp-an-introduction/]
What are preventive measures and controls for food safety?
From Codex’s definition, food safety control measure means “any action and activity that can be used to prevent or elminate a food safety hazard or reduce it to an acceptable level.”
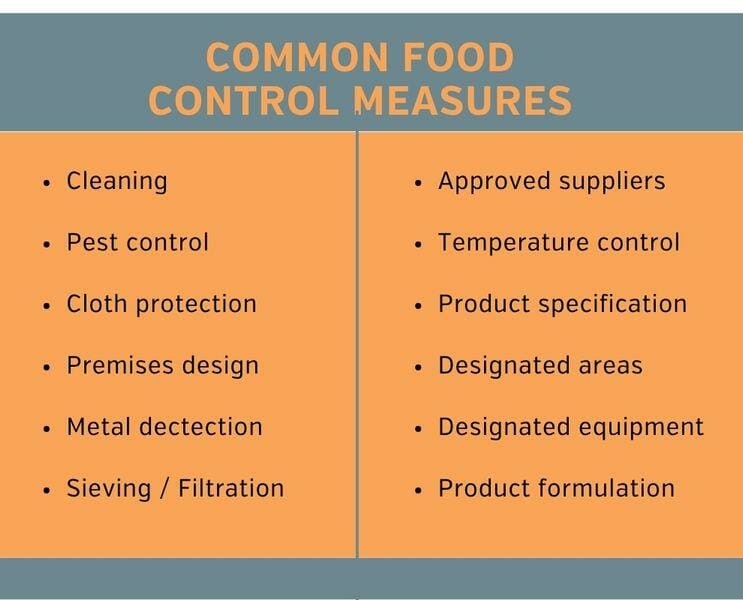
Control measures are under three categories: prerequisite programmes (PRP), operational prerequisite programmes (OPRP) and critical control points (CCP)(extended reading: understanding the difference between PRP, OPRP and CCP). To review the control measures and keep everything documented, food safety management software can help you construct your HACCP plans and control the risk effectively.
How can we prevent foodborne illness effectively?
While individuals can proceed with 4 steps to prevent foodborne illness, businesses face more significant challenges. Some companies may lack the necessary resources or knowledge to implement comprehensive scientific methods and practices for prevention. Still, it is incumbent on all of us involved in food manufacturing to create a safe environment for the handling, preparation, and storage of food in a manner to prevent foodborne illnesses. Reading through the FDA Codes of Federal Regulations , you will undoubtedly find an incredible amount of sleep-inducing reading. However, you will also find several keys to manufacture, pack, hold and ship food for human consumption. You can also look at different food safety systems like HACCP, FSMA, and GFSI, each of which will dive deeper into the specific elements required to ensure food safety. An argument can be made regarding which methods/elements are the best, but we will focus on a few synonymous foundational pillars.
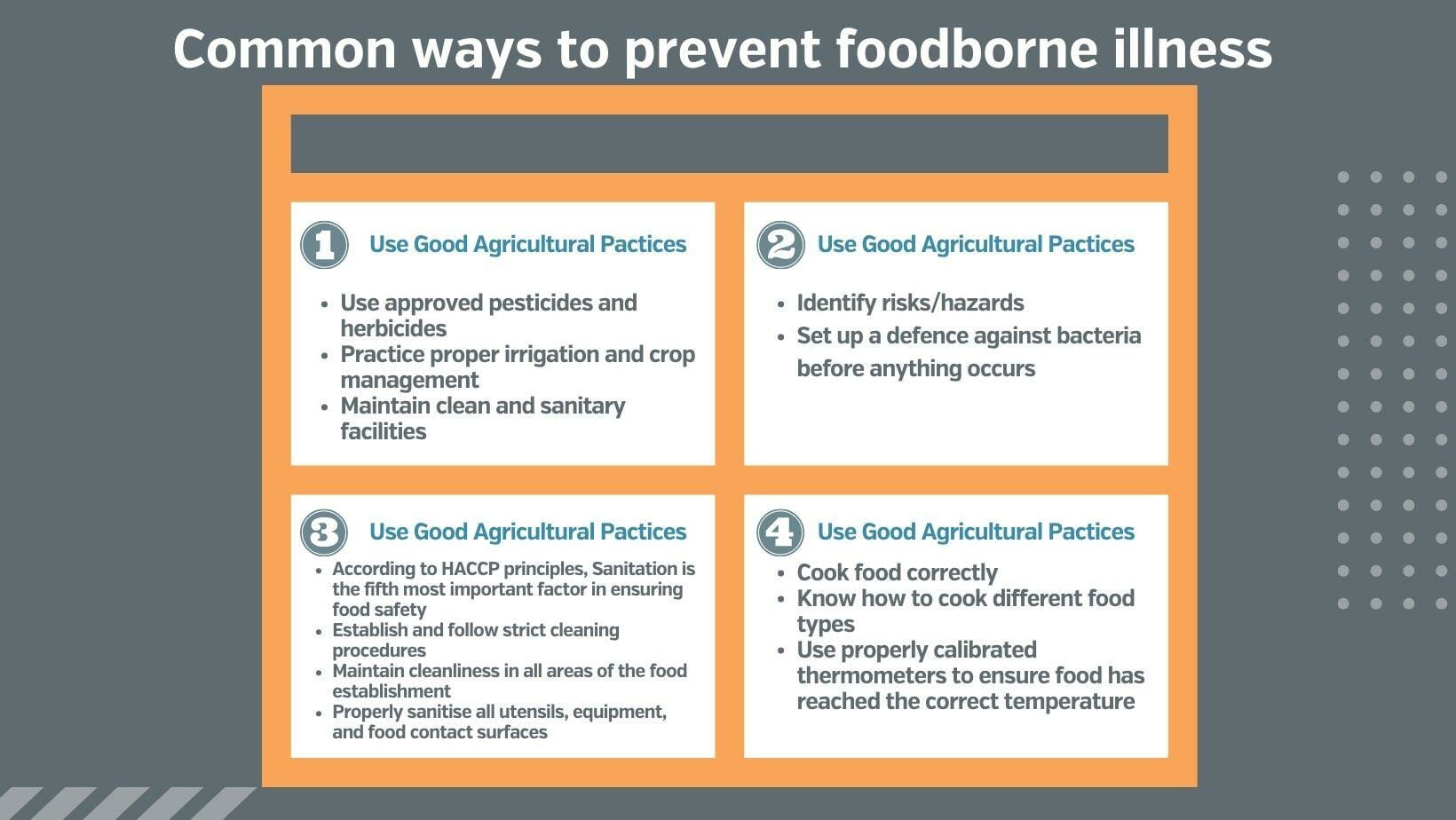
1. Use Good Agricultural Practices
-
- Use approved pesticides and herbicides
- Practice proper irrigation and crop management
- Maintain clean and sanitary facilities
2. Develop and Implement Food Safety Plans
-
- Identify risks/hazards
- Set up a defence against bacteria before anything occurs
3. Maintain Good Hygiene Practices, Including Plant Sanitation
-
- According to HACCP principles, Sanitation is the fifth most important factor in ensuring food safety
- Establish and follow strict cleaning procedures
- Maintain cleanliness in all areas of the food establishment
- Properly sanitise all utensils, equipment, and food contact surfaces
4. Follow Proper Cooking Methods
-
- Cook food correctly
- Know how to cook different food types
- Use appropriately calibrated thermometers to ensure food has reached the correct temperature
Improving food safety benefits customers and protects anyone downstream of the manufacturing process which handles food. It can also protect people and animals exposed to foodborne illnesses that may have been inadvertently introduced into the food. A food manager must ensure written instructions are available for which of the following steps to produce safe foods and help keep your products clean:
6 Ways to reduce food safety risk
1. Execute management commitment
People may think this is not a preventative measure. However, if management is not committed to food safety, it can completely derail your food safety program. The food industry has experienced its fair share of examples when control intentionally overrides food safety policies and procedures. It doesn’t have to be a systemic issue that has repeated itself over a substantial period – for a food safety issue with deadly results, there only needs to be a single occasion where food safety practices were ignored. Food safety practices are a top-down process.
2. Construct your food safety plan
Creating a robust food safety plan is an integral preventative measure for food safety. All food businesses should have a written food safety plan that outlines the specific procedures and practices that will be followed to ensure safe food handling. Your legislative authority typically requires an adequate food safety plan (download our “Developing a Food Safety Plan Under FSMA” or read an in-depth analysis of the difference between HACCP and HARPC for a detailed in-depth analysis of the difference between HACCP and HARPC for detail guide).
Regardless of the “brand” of food safety plan you choose, here is the checklist of writing a food safety plan:
- Identify and describe the product/process
- Outline the process and construct a flow diagram
- Analyze the potential hazards/risk at each step in the process
- Determine science-based critical limits and monitor the process
- Determine corrective actions and apply them
- Validate your decisions
3. Educate your employee with the best practice of food safety knowledge
Employee knowledge is critical for preventing food safety issues. Food safety training should cover basic hygiene, food handling procedures, and proper cooking/processing techniques. Employees should also be aware of the potential hazards associated with various food items.
In addition to formal training, employees should also be encouraged to ask questions and seek clarification when unsure. An open communication culture will help ensure that potential problems are quickly identified and addressed.
4. Sanitise equipment and procedures
Preventing foodborne illness starts with cleanliness. Washing hands thoroughly, keeping food preparation areas clean, and cooking food to the proper temperature are all essential steps in preventing foodborne illness.
Cleaning and sanitising are critical preventative measures for food safety. All surfaces that come into contact with food must be cleaned and sanitised regularly. This includes utensils, conveyor belts, holding hoppers, can tracks, filling machinery, packaging machinery, and other equipment or surfaces that come into contact with food.
Cleaning is the first step in the process and involves removing all dirt, debris, and contaminants from the surface. This is typically done in a conventional food system with hot water and a commercial cleaning solution applied at a prescribed dose. Once the surface is clean, it must be sanitised to kill any remaining bacteria or viruses. (it should go without saying that when mixing any solutions, it is essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions!)
The typical sanitation process would be to mix (if necessary) the proper solutions. Once applied, they need to sit on the surface to achieve the recommended contact/dwell time. Surfaces then can be rinsed with a deluge of water before coming in contact with food. A sanitation activity can be verified through a visual inspection. However, a more effective means of verification, like a chemical concentration or ATP test, might be required.
Cleaning and sanitising are critical preventative measures for food safety. All food contact surfaces must be cleaned and sanitised before each use to prevent the spread of foodborne illness.
5. Pest Control
Analysis of SQF non-conformances from unannounced audits in 2019 by the Safe Food Alliance found that clause 11.2.12.2, pest prevention (identified as pest activity), was in the top 10.
Proper pest management is required in manufacturing/storage facilities to ensure no pests enter the product, however, it is important to clarify that the term ‘pests’ is not exclusively applied to organisms in proximity of a factory, but also includes insects and other lifeforms that can enter a food processing facility through the supply chain.
Once entered, the buildings often provide shelter, warmth, food, water, and safety from predators, all of which can serve as ideal conditions for proliferation, so it is necessary to remain vigilant.
All potential sources of contamination, including pests, must be controlled to help prevent the spread of disease-causing bacteria or other contaminants. Safefood 360° has Pest Control Module to help food safety managers to execute HACCP effortlessly.
6. Proper Cooking and Holding Temperatures
Cooking food to the proper temperature and then holding it at that temperate is one of the most important preventative measures to ensure food safety. Undercooked food can harbour harmful bacteria that can cause severe illness and even death. Food that is properly cooked but not held at the proper temperature after cooking can become dangerous.
Pasteurization and sterilization are two of the main processes for thermal processing. Previously, we’ve covered several different processing techniques, such as the thermal processing guide and webinar about thermal processing in food industry.
Safefood 360° is an innovative software designed by food experts, and it is dedicated to food manufacturers to work for a safer world. Subscribe to our newsletter for the latest food safety news. If you would like to have more details about how to ensure the food safety of your company, submit a demo request here.





Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!